This article reviews antifungal agents currently in various stages of clinical development. Those with two nitrogens in the azole ring the imidazoles.

Current Status And Structure Activity Relationship Of Privileged Azoles As Antifungal Agents 2016 2020 Sciencedirect
Furthermore this work aims to critically review azole antifungal resistance among environmental isolates of fungal species predominant molecular mechanisms of azole resistance in the environment and the implications for human health.

Azole antifungal review. Purpose of review With the introduction of new targeted therapies for hematological malignancies comes the challenges of both assessing the risk of developing an IFD while being treated with these agents as well as managing the drug--drug interactions between azole antifungals and the agents. The azoles interfere with the synthesis and permeability of fungal cell membranes by inhibiting cytochrome P450-dependent 14-alpha-sterol demethylase. The drug interactions mentioned below are not intended as a complete listing.
However reversible alopecia is not uncommon with this agent 52. This article reviews antifungal agents currently in various stages of clinical development. New additions to existing antifungal classes will be discussed including SUBA-itraconazole a highly bioavailable azole and amphotericin B cochleate an oral amphotericin formulation as well as.
Azoles are the most commonly used antifungals in the c linical treatment of local and systemi c fungal infections. Triazole compounds containing one or more 124-triazole rings. Clinicians should refer to a specific drug interaction reference before using azole antifungal drugs.
Pearls. There is however extensive documentation of intrinsic and developed resistance to azole antifungals among several Candida species. A Brief Review of Antifungal Drugs Old and New Introduction Invasive fungal infections caused by opportunistic organisms such as Candida and Aspergillus species are of significant concern as the population of immune compromised patients in society today rises 1-4.
Azole antifungals are a group of medicines that contain an azole ring and inhibit the growth of a wide range of fungi. Similar to azole antifungal agents the allylamine terbinafine inhibits ergosterol biosynthesis by inhibiting squalene monoxygenasean enzyme in fungi responsible for conversion of squalene to squalene epoxide which is a precursor to lanosterol in the ergosterol synthesis pathway. Examples include clotrimazole econazole ketoconazole miconazole and tioconazole and those with three nitrogens in the azole ring the triazoles.
Herein the description of the target salient medicinal chemistry points regarding azole structures SAR and the selectivity of these structures for. New additions to existing antifungal classes will be discussed including SUBA-itraconazole a highly bioavailable azole and amphotericin B cochleate an oral amphotericin formulation as well as rezafungin a long-acting echinocandin capable of once. 1 Drug prescription during pregnancy requires a delicate assessment of the balance between maternal benefit and fetal.
20 Although allylamines do not seem to have the same collateral effects on human CYP enzymes. This review describes present and future uses of the currently available azole antifungal agents in the treatment of systemic and superficial fungal infections and provides a brief overview of the current status of in vitro susceptibility testing and the. Fungi are common pathogens in critically ill or immunosuppressed patients.
In this paper we provide a comprehensive review and an update of all approved and clinical candidates of azole antifungal drugs as azole pedigree in regard to their structural similarities. Mixed reviews for how well it works on tough fungal infections such as ringworm. Azoles are considered as one of the most efficient fungicides for the treatment of humans animals and plant fungal pathogens.
The higher solubility of the drug in the vehicle may result in higher thermodynamic activity and thus greater partitioning into the skin and increased bioavailability of antifungal in the skin 25 for example sertaconazole anhydrous gel. History of the development of antifungal azoles. Pregnancy should be considered as a condition with increased vulnerability to infections including some life-threatening fungal infections but paradoxically little is known regarding optimal antifungal regimens and dosages in this setting.
This article will briefly review the mechanisms of action spectrum of activity pharmacodynamics pharmacokinetics and safety of the most commonly used antifungal agents in clinical practice. 5 tubes for one price also makes this pick an awesome deal. Azole antifungals such as fluconazole are often preferred treatment for many Candida infections as they are inexpensive exhibit limited toxicity and are available for oral administration.
Fungal infections mycoses though not as. The newest antifungal class the echinocandins was introduced in 2001 with cas-pofungin. With 1 Clotrimazole one of the most effective anti-fungal medications it tackles problem areas and soothes itching.
Azole antifungals consist of two primary classes. Review all concurrent drug use before prescribing them. A review on structures SAR and mechanism of action With the increasing risk of invasive and life threating fungal infections there is now a great concern regarding the lower discovery rate of antifungal drugs.
The newest azole released in 2015 isavuconazole has similarly broad activity with more favorable pharmacologic properties allowing for improved bioavailability more predictable drug levels and fewer drug interactions. They are classified into two groups. An anhydrous vehicle may be preferred as a topical vehicle for azole antifungals.
A review Abstract Invasive fungal infections and systemic mycosis whether from nosocomial infection or immunodeficiency have. Topical therapy for fungal infection is advantageous because the drugs are. The present review aims to explore the pharmacology pharmacokinetics spectrum of activity safety toxicity and potential for drugdrug interactions of the azole antifungal agents.
They are of significant clinical importance as antifungal drugs and are widely used in personal care products ultraviolet stabilizers and in aircraft for its anti-corrosive properties. Both classes are fungistatic agents and share similar mechanisms of action. Azole antifungal agents Fluconazole is an extremely well-tolerated agent that lacks significant toxicity despite having been used for treatment and prophylaxis in many patient populations for more than a decade.
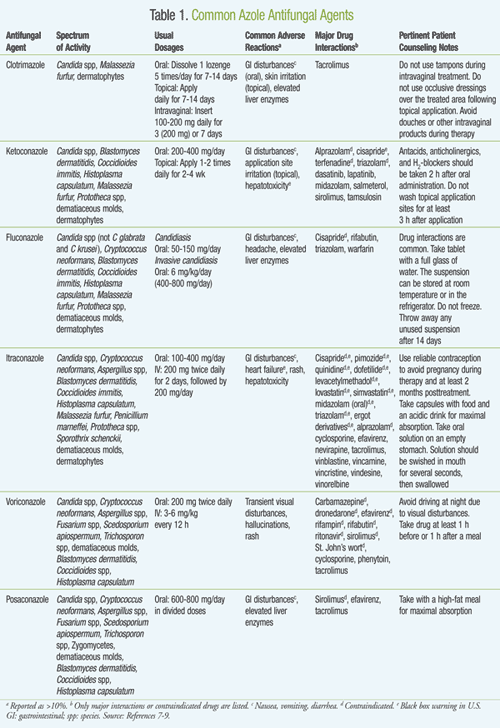
Azoles For over two decades the azole antifungals have been used in clinical practice to treat various fungal infections TABLE 1. Becoming resistant to current antifungal medications is of appreciable concern.
The Fungus Among Us An Antifungal Review